How Is Orbital Hybridization Useful in Describing Molecules
In this video we use both of these methods to determine the hybridizations of atoms in various organic molecules. 12-03-2022 This browser does not support the video element.
Are There Atomic Not Molecular Electron Orbitals That Lack Any Reflective Symmetry Quora
The molecules are said to be more stable because they are hybrids resonance hybrids of these different electron arrangements called contributors.

. The form of the molecule may be predicted if the hybridization of the molecule is understood. As with carbon atoms nitrogen atoms can be sp3 - sp2 or sphybridized. Hybridization occurs only at some stage in the bond formation and not in an isolated gaseous atom.
In this theory we are strictly talking about covalent bonds. In other compounds. According to the theory covalent shared electron bonds form between the electrons in the valence orbitals.
In CO 2 determine the hybridization of the oxygen atoms. Describe the bonding Hybridization in N2 O2 Cl2 CO2 and H2O. The Valence Bond Theory is the first of two theories that is used to describe how atoms form bonds in molecules.
Hybridization is the process of mixing two or more atomic orbitals to create new covalently bonded orbitals in molecules. How is orbital hybridization useful in describing molecules. LEARNING OBJECTIVES To introduce the basic principles of molecular orbital theory and electronic geometry of molecules.
Draw the energy levels and name the orbitals formed in this hybridization. Hybridized orbitals are very useful in explaining of the shape of molecular orbitals for molecules and are an integral part of valence bond theory. Draw the hybridized orbital for each molecules.
The valence orbitals of a central atom surrounded by five regions of electron density consist of a set of Blank sp2d hybrid orbitals. Hybrid orbitals are very useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and. Describe the bonding Hybridization in N2 O2 Cl2 CO2 and H2O.
In chemistry hybridization or hybridisation is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. In linear molecules like CO 2 the central atom has only two equivalent bonding orbitals. Note that in this course the term lone pair is used to describe an unshared pair of electrons.
Each blank can be completed with a term short. Hybridised orbitals are very useful in the explanation of the shape of molecular orbitals for molecules. See also what is maritime tropical.
To generate alternate electron arrangements. Hybridized orbitals are useful in explaining the shapes of and types of bonding in molecules. Orbital hybridization provides information about both molecular bonding and molecular shape.
Molecules for which several different nearly equivalent structures can be drawn are said to be resonance-stabilized. In methane CH 4 for example a set of sp 3 orbitals forms by mixing one s- and three p-orbitals on the carbon atom. When two sp hybridized atoms come together to form bonds as in acetylene H-CC-H the sp orbitals overlap end-on.
This theory is especially useful to explain the covalent bonds in organic molecules. Fill in the electrons for carbon and determine the number and typed of bonds formed. However hybrid orbitals and pure atomic orbitals have different.
Place to form molecules. PFS Part 2 Using orbital diagrams show how sp hybrid orbitalls are formed from 2s and 2p orbitals in carbon Part 3 Using Molecular Orbital Theory explain why diatomic oxygen O2 contains both. They form the σ framework of the molecule.
It is an integral part of valence bond theory. For example we can use orbital hybridization to understand why methane has the formula CH₄ how the overlap of carbon and hydrogen atomic orbitals is used to form electron-pair bonds and why the arrangement of the C-H bonds about the central carbon is tetrahedral. Molecular Orbital Theory an alternative theory does not need hybridization at all.
Construct the Robert structure of CH_3CN. This is the currently selected item. The hybrids are named for the atomic orbitals involved in the hybridization.
In this lecture we Introduce the concepts of valence bonding and hybridization. This hybridization gives trigonal planar geometry. How do electronegativity values determine the charge distribution in a polar covalent bond.
The orbitals are directed toward the four. In chemistry hybridisation is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals suitable for the qualitative description of atomic bonding properties. The p orbitals overlap side-on to form π bonds at 90 angles to each other.
Which orbital hybridization may be used to describe the carbon atoms 1 2 3 and 4 in But-1-en-3-yne. Draw the hybridized orbital for each molecules. Concluding orbital is an approximate depiction of electron distribution in polielectronic atoms and molecules and despite its limitations it can give valuable insights about chemical and physical properties.
ORBITAL HYBRIDIZATION THEORY If we look at the valence shell configuration of carbon we find two paired electrons in the 2s orbital and two unpaired electrons in the 2p X and 2p Y orbitals one in. Moreover there are theories that do not even consider orbitals in their formalism. In chemistry orbital hybridisation or hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals with different energies shapes etc than the component atomic orbitals suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theoryFor example in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital combines.
Hybridization is a concept used in organic chemistry to explain the chemical bonding in cases where the valence bond theory does not provide satisfactory clarification. Part 1 Describe the hybridization type molecular shape and bond angle in each of these molecules. The bigger lobe of the hybrid orbital constantly has a high-quality sign at the same time as the smaller lobe on the other facet has a bad sign.
The valence-bond concept of orbital hybridization can be extrapolated to other atoms including nitrogen oxygen phosphorus and sulfur. Up to 24 cash back Describe how VSEPR theory helps predict the shapes of molecules Identify the ways in which orbital hybridization is useful in describing molecules Vocabulary Part ACompletion Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are introduced in this section. We can find the hybridization of an atom in a molecule by either looking at the types of bonds surrounding the atom or by calculating its steric number.

High School Chemistry Orbital Configurations Aufbau Principle High School Chemistry Chemistry
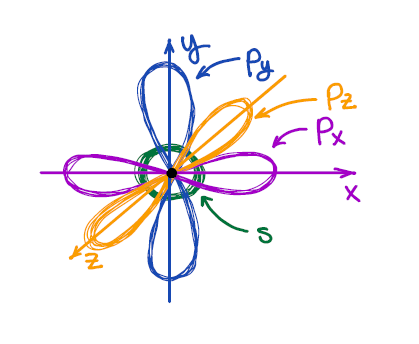
Hybridization Organic Chemistry Tutor

Hybridization Of Ch4 Description Of Hybrid Orbitals For Carbon Youtube
How Co Forms According To Molecular Orbital Theory Please Clarify The Concept Of Hybridization Involved In This According To Molecular Orbital Theory Quora

Coordination Compound Ligand Field And Molecular Orbital Theories Britannica

Orbital Chemistry And Physics Britannica

Pdf On The Role Of D Orbital Hybridization In The Chemistry Curriculum

The Mo Description Of Sf 6 18 Involves A Combination Of The Sulfur 3s Download Scientific Diagram
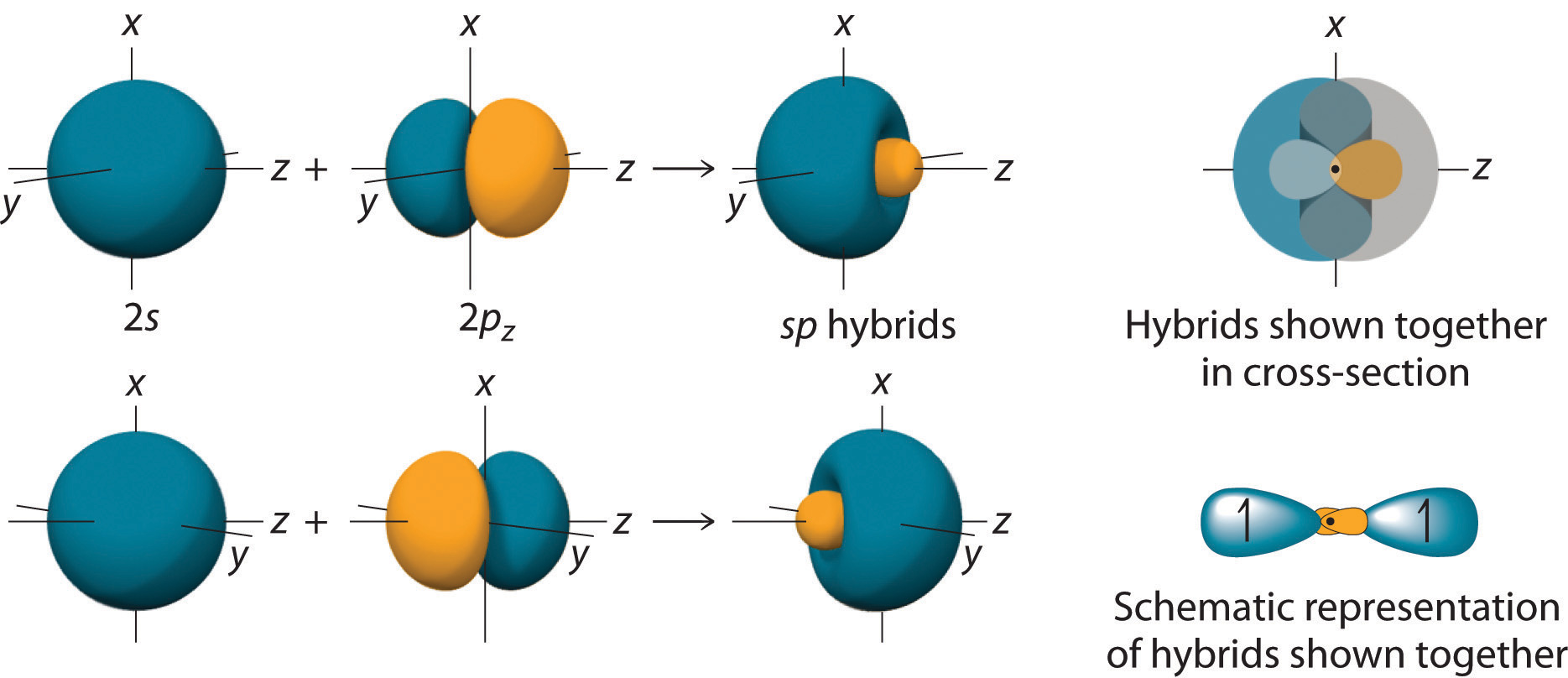
10 7 Valence Bond Theory Hybridization Of Atomic Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts

Hybridization Of Cl2 Description Of Hybrid Orbitals For Chlorine Youtube
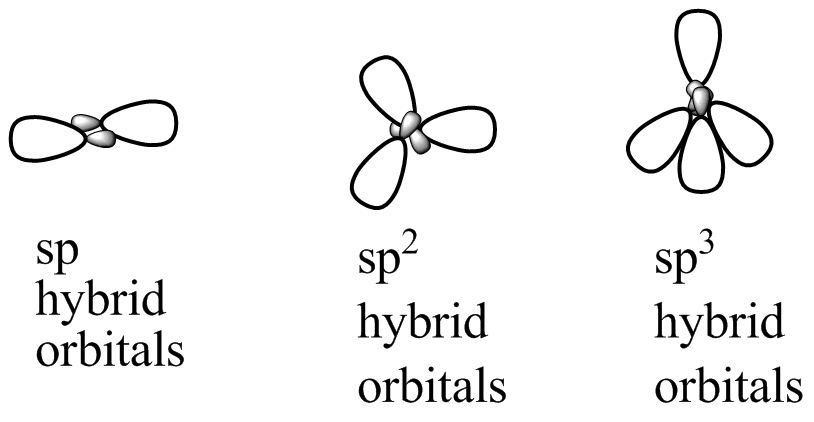
Hybrid Orbitals Sp Study Guide Inspirit
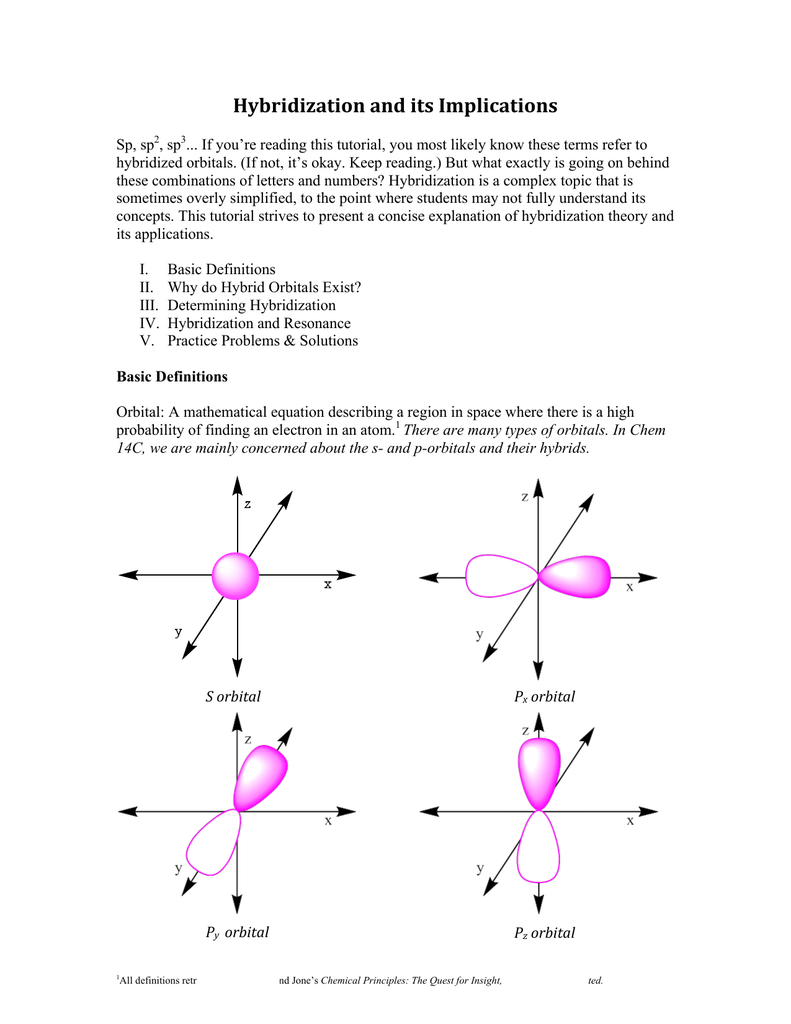
Hybridization And Its Implications
Why Do Orbitals Hybridize Does Hybridization Occur In Every Molecule Quora

Pdf On The Role Of D Orbital Hybridization In The Chemistry Curriculum
What Is An Explanation Of The Hybridization Of Orbitals Quora

Hybrid Orbitals Chemistry For Non Majors

Orbital Chemistry And Physics Britannica

Ionic Vs Covalent Bonds Ionic Vs Covalent Bonds Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonds

Comments
Post a Comment